The post-Brexit trade deal between the UK and EU takes effect at 23:00 GMT on Thursday, after it was signed into law.

Parliament overwhelmingly backed the agreement in a high-speed process on Wednesday, following the two sides reaching agreement on Christmas Eve.
The UK leaves the EU’s single market and customs union, but the deal ends the possibility of tariffs on goods.
PM Boris Johnson thanked MPs and said: “The destiny of this great country now resides firmly in our hands.”
But opponents say the country will still be worse off than it was while in the EU.
Brexit happened on 31 January, but the UK has continued to follow Brussels’ trade rules until now.
The deal – reached just before the deadline to do so – sets out a new business and security relationship, following the severing of these ties.
It comes four-and-a-half years after the UK voted to leave the EU in a referendum.
- A Brexit deal has been agreed, days before a deadline. It means that the UK and the EU can continue to trade without extra taxes being put on goods.
- What took so long? The UK voted to leave the EU in 2016 and actually left on 31 January 2020, but leaders had until the end of 2020 to work out a trade deal.
- There are big changes ahead. Although it’s a trade deal that has been agreed, there will also be changes to how people travel between the EU and UK, and to the way they live and work.
The EU (Future Relationship) Bill, bringing the trade deal into UK law, was backed in its first parliamentary stage in the House of Commons by 521 to 73 votes on Wednesday, after Parliament was recalled from its Christmas break.
The House of Lords later passed it at third reading – its final stage – without a vote and the Queen – who is spending the festive period at Windsor Castle rather than Sandringham because of the coronavirus pandemic – gave the final approval, Royal Assent.
In an interview with the BBC’s Laura Kuenssberg, the prime minister said the deal would allow the UK to “go our own way but also have free trade” with the EU.
Most Labour MPs voted in favour after leader Sir Keir Starmer said a “thin deal was better than no deal”.
But all other opposition parties, including the SNP, the Lib Dems, Plaid Cymru and all Northern Ireland parties that take seats at Westminster, opposed the bill.
European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen and European Council President Charles Michel signed the deal earlier on Wednesday in Brussels smiling at a brief televised ceremony to put their names to the 1,246-page Trade and Cooperation Agreement in Brussels.
“It has been a long road. It’s time now to put Brexit behind us. Our future is made in Europe,” von der Leyen said.
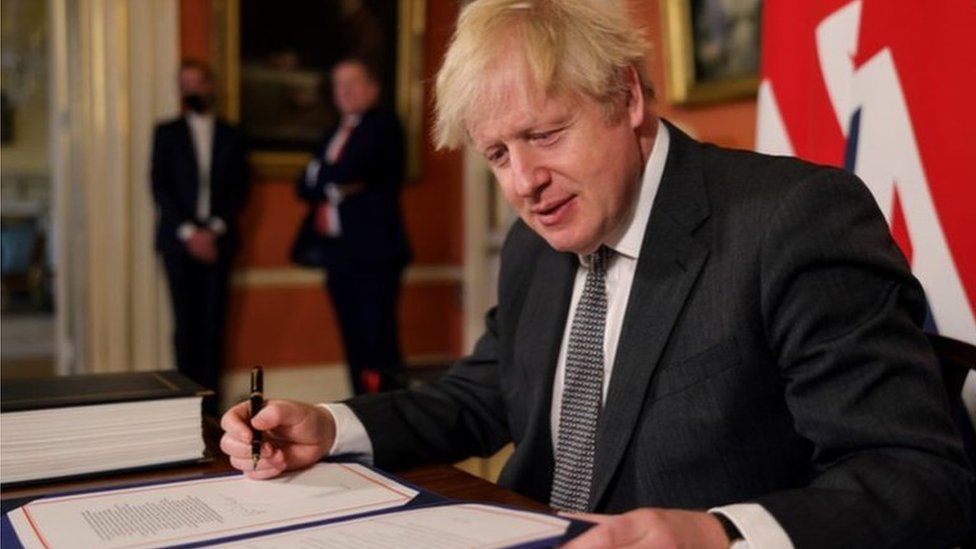
The leather-bound document was then flown by the Royal Air Force to London for Prime Minister Boris Johnson to add his signature, as the UK parliament held a rushed debate to ratify the deal in the dwindling time left.
Johnson gave a thumbs up after inking what he described as “the beginning of what will be a wonderful relationship between the UK and our friends and partners in the EU”.
Britain will leave the European single market and customs union at 11:00 pm (2300 GMT) on Thursday, the end of a post-Brexit transition period marked by tortuous trade negotiations which culminated in the Christmas Eve deal.
Introducing an 85-page bill to implement the pact, Johnson told the House of Commons that it heralded a new chapter for Britain and the EU as “sovereign equals, joined by friendship, commerce, history, interests and values”.
The lower house voted overwhelmingly by 521-73 to back the deal, despite serious opposition misgivings, and the bill then passed the House of Lords late Wednesday in an unusually rapid one-day procedure.
London and Brussels would work “hand in glove whenever our values and interests coincide, while fulfilling the sovereign wish of the British people to live under their own sovereign laws made by their own sovereign parliament”, Johnson added.
Anxious wait
Michel echoed the sentiment in Brussels, vowing the two sides would work “shoulder to shoulder” on major issues, including climate change and future health pandemics.
Johnson’s government only published the accompanying UK legislation on Tuesday afternoon, less than 24 hours before the debate began in parliament, underscoring the frantic dash to clear the decks in time.

The last-ditch deal averted the prospect of a cliff-edge separation which would have seen quotas and tariffs slapped on all cross-Channel trade, exacerbating strains in the middle of the coronavirus pandemic, which has hit Britain harder than most.
But British fishermen have accused the government of selling them out, while services — accounting for 80 percent of the UK economy — were largely omitted.
The City of London financial hub faces an anxious wait to learn on what basis it can continue dealing with Europe in the future.
Theresa May, whose three-year Brexit-dominated premiership ended in 2019 after she failed to win support for a closer future relationship with the bloc, voiced unease.
“We have a deal in trade which benefits the EU, but not a deal in services which would have benefited the UK,” she told MPs.
‘Thin deal’
However, an influential faction of arch-Brexiteers in Johnson’s ruling Conservatives gave their blessing to the EU agreement on Tuesday, and the main opposition Labour party also gave its reluctant backing.
“This is a thin deal, it’s got many flaws, but a thin deal is better than no deal,” Labour leader Keir Starmer told MPs, accusing other opposition parties of staging an irresponsible protest vote.
Lawmakers from the pro-European Liberal Democrats and Scottish National Party voted against — with the SNP using the issue to push for a fresh referendum on independence for Scotland.
In Edinburgh, the SNP-dominated Scottish Parliament declined to give its own consent to the Brexit deal, although First Minister Nicola Sturgeon acknowledged that would not affect passage of the UK bill.
The agreement’s impact will play out in the coming months, with UK businesses braced for customs red tape they have avoided for decades in cross-Channel trade.
Meanwhile from January 1, there will no longer be free movement of people from Britain to the EU or vice versa.
Under the compressed legislative calendar, the European Parliament will debate the Brexit deal after the New Year, but is expected to eventually nod it through.
Pending that, EU member states gave their green light on Monday for the accord to take provisional effect before the New Year’s Eve deadline.
It will come into force at 23:00 on Thursday, but although the European Parliament has begun its scrutiny of the 1,246-page document, it will not get a chance to ratify it formally until early in the new year.
The deal has, however, been given the unanimous backing of ambassadors from the 27 nations and the member states gave their written approval on Tuesday